¶ Description
Model factory.
¶ Parameters
¶ Parameters tab
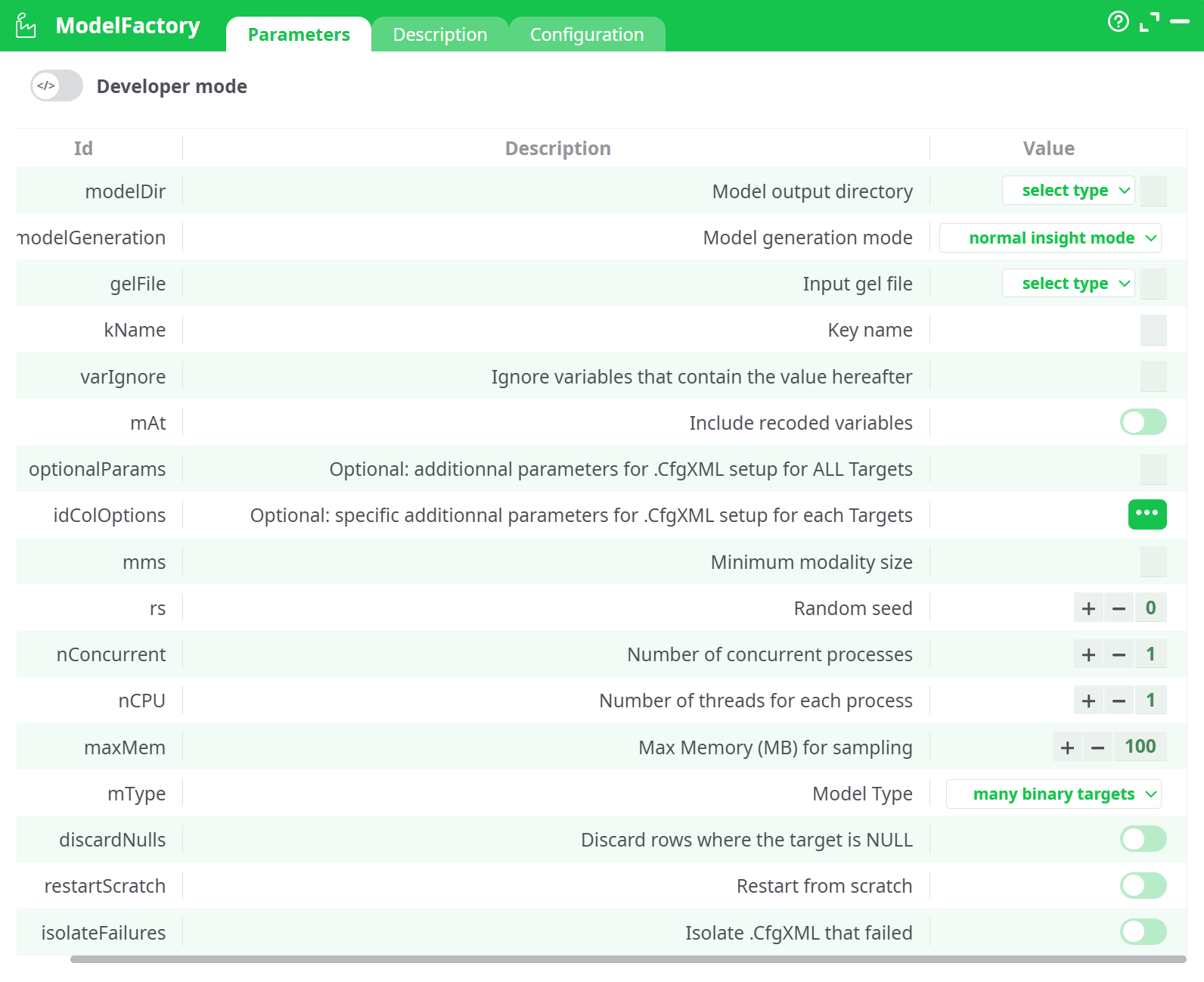
Parameters:
- Developer mode: activate/deactivate code tab.
- modelDir: model output directory
- modelGeneration: model generation mode
- getFile: input gel file
- kName: Key name
- varIgnore: Ignore variables that contain the value hereafter
- mAt: Include recoded variables
- optonalParams: optional, additionnal parameters for .CfgXML setup for ALL Targets
- idColOption: optional, specific additionnal parameters for .CfgXML setup for each Targets
- mms : minimum modality size*
- rs: random seed**
- nConcurrent: number of concurrent processes
- nCPU: number of threads for each process
- maxMem: max memory (MB) for sampling
- mType: Model Type
- discardNulls: discard rows where the target is NULL
- restartScratch: Restart from scratch
- isolateFailures: Isolate .CfgXML that failed
¶ Description tab
See dedicated page for more information.
¶ Code tab
ModelFactory is a scripted action. Embedded code is accessible and customizable through this tab.
¶ Configuration tab
See dedicated page for more information.
¶ About
This action trains and packages predictive models from a single input dataset. It’s designed for quick “factory-style” model generation with sensible defaults, but still gives you levers for performance, reproducibility, and resource control.
¶ What goes in / what comes out
Input (gelFile)
A single tabular dataset you select from:
- assets – files you uploaded to the project
- temporary data – upstream action output from the current run
- recorded data – persisted run outputs
- JavaScript expression / Sources / Disk images – advanced paths/mounts (use only if you already rely on them)
Output
- A model bundle in the subfolder named by modelDir (the “model tag”).
Typically includes model config (CfgXML), learned parameters, and run logs/metrics per target.
¶ Quick-start recipe (recommended)
-
gelFile: pick your training table.
-
modelDir: short, URL-safe tag (e.g.,
churn_v1). -
modelGeneration: keep normal insight mode to balance quality and speed.
-
mType (Model Type):
- many binary targets – one binary model per boolean/0-1 target column.
- one multi-class target (per segment) – a single multiclass target (optionally segmented).
- one continuous target (per segment) – a regression target (optionally segmented).
-
(Optional) kName: set the unique row key if your table has one (e.g.,
id). -
(Optional) varIgnore: list columns to drop (comma-separated) – e.g.,
id, created_at, notes. -
Run with defaults first. If it fits memory/time, you’re good; otherwise tune nCPU, nConcurrent, maxMem.
¶ Parameters (what they do & when to touch them)
¶ Data and generation
-
gelFile (required) – source dataset.
-
modelDir (required) – subfolder/tag for artifacts (becomes the output directory name).
-
modelGeneration – strategy:
- normal insight mode (default): good quality + reasonable time.
- fast insight mode: smaller search; good for prototyping or large iterations.
- performance mode: deeper search; expect longer runtimes and more memory use.
-
kName – primary key column (optional, but helpful for traceability).
-
varIgnore – columns to exclude; use for IDs, free-text blobs, leakage columns, etc.
-
mAt (Include recoded variables) – when ON, allows auto-generated encodings/derivations to be considered alongside raw variables.
¶ Per-target & per-column overrides
- optionalParams – advanced, applied to all targets. Leave empty unless you know the exact CfgXML flags you want to enforce.
- idColOptions – advanced, per column options (e.g., force type, special handling). Keep empty unless you depend on a known house style.
¶ Data hygiene & sampling
- mms (Minimum modality size) – minimum category frequency to keep as its own level; rare categories are grouped. Start with 1; raise it if you have many singletons.
- discardNulls – when ON, rows with NULL target are removed (predictors with nulls are still OK). Recommended ON for supervised tasks.
¶ Reproducibility & resources
- rs (Random seed) – set a fixed integer to make runs reproducible.
- nConcurrent – how many targets to train at once (pipeline-level parallelism). Start with 1 unless you’re sure you have headroom.
- nCPU – threads per training process. If you have 8 vCPUs: use nConcurrent=1, nCPU=4–8.
- maxMem (MB) – hard cap per process. Default 100 MB is conservative; raise carefully if your data is large (e.g., 1024 for 1 GB).
- restartScratch – when ON, ignores previous artifacts in modelDir and builds from zero.
- isolateFailures – when ON, failing targets write isolated CfgXML for debug and do not kill the whole batch.
¶ Model Type (mType) — pick the right training target pattern
- many binary targets (default)
Trains one binary classifier per eligible target column (e.g.,churn,responded). Ensure targets are boolean or clearly 0/1. - one multi-class target (per segment)
Trains a multiclass model on the single target you designate upstream (or via column options). Great for labels likestatus ∈ {new, active, churned}. - one continuous target (per segment)
Trains a regression model for a numeric outcome (e.g.,LTV,amount). Handle outliers/nulls before training for best stability.
¶ Typical workflows
¶ A) Many binary KPIs at once
- mType: many binary targets
- varIgnore:
id, note_text - discardNulls: ON
- Outcome: Separate model + metrics per binary target; artifacts saved under modelDir.
¶ B) Single multiclass model
- Prepare dataset with one label column (e.g.,
stage). - mType: one multi-class target (per segment)
- (Optional) Provide a segment column upstream if you want per-segment models.
- Review confusion matrix & per-class metrics in the output.
¶ C) Regression
- Ensure target (e.g.,
amount) is numeric; treat outliers upstream. - mType: one continuous target (per segment)
- Inspect R² / MAE / RMSE artifacts in the model folder.
¶ Performance & stability tips
- Memory: If you see OOM or aggressive swapping, lower nConcurrent or nCPU, or raise maxMem modestly.
- Cardinality: If training slows on wide categoricals, raise mms (e.g.,
5or10) to group rare levels. - Leakage: Add timestamps and future info to varIgnore.
- Reproducibility: Always set rs once you lock a run for documentation or audit.
- Fresh starts: If you changed schema/targets, toggle restartScratch to avoid stale artifacts.