¶ Description
Compute centrality measures in a social graph.
¶ Parameters
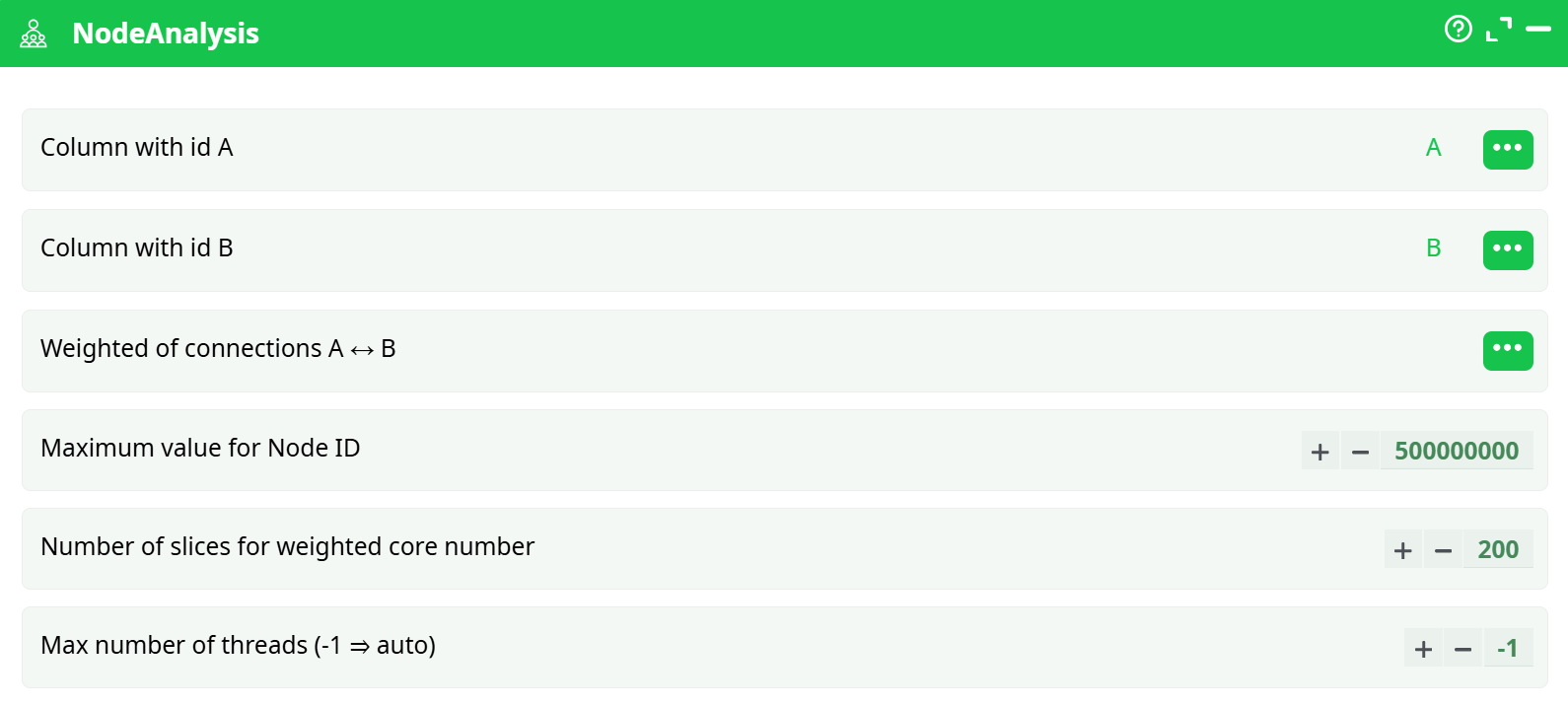
Parameters:
- Column with id A
- Column with id B
- Weighted of connections A<->B
- Maximum value for Node ID
- Number of slices fr weighted core number
- Max number of threads (-1 = auto)
¶ About
The NodeAnalysis action button performs advanced structural analysis on a graph by calculating key metrics per node, including:
- Social Degree
- Core Numbers (standard and weighted)
- Social Leadership indicators
It is particularly useful in social network analysis, graph theory, and community behavior studies, providing insight into node influence, position, and network cohesion.
¶ Inputs
The action requires a dataset that describes connections between nodes in a graph structure, typically formatted with columns:
A— Node ID of the source nodeB— Node ID of the target nodeWeight— Weight of the connection between A and B
¶ Output
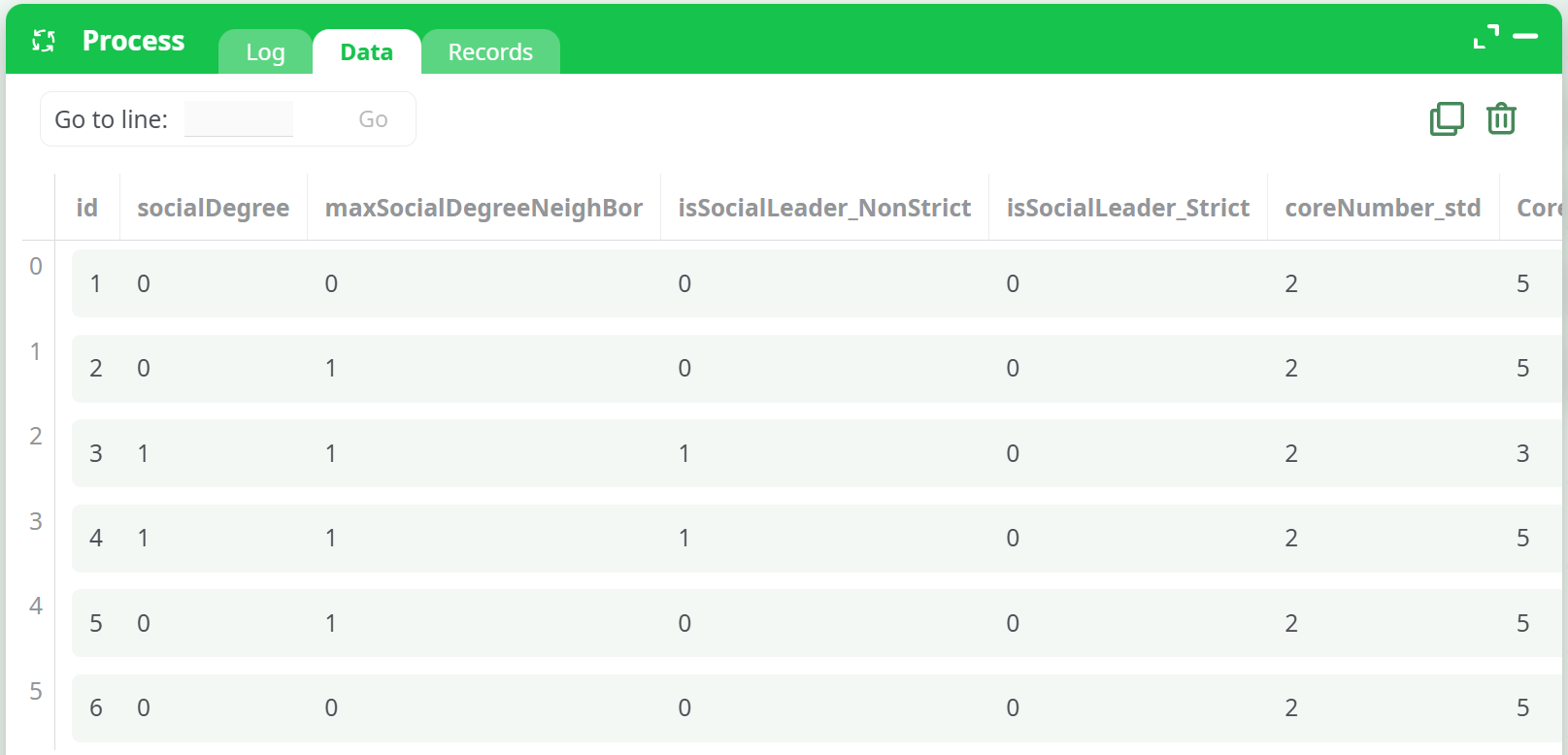
The output is a dataset enriched with several graph metrics:
socialDegree: Number of direct connections per node.maxSocialDegreeNeighbor: Maximum degree of neighboring nodes.isSocialLeader_NonStrict: Node is a non-strict leader (based on certain heuristics).isSocialLeader_Strict: Node is a strict leader (stricter thresholds).coreNumber_std: Standard core number for the node.CoreNumber_weighted: Weighted core number using the provided edge weights.
¶ ▶️ How to Run
- Connect an
InlineTable,ReadCSV, or any table source containing node-to-node connections. - Drag the
NodeAnalysisaction button onto the canvas. - Set the following columns:
Column with id A: Source node columnColumn with id B: Target node columnWeighted of connections A ↔ B: Connection weight column
- Adjust optional parameters if necessary:
- Keep
Max number of threads = -1for auto-parallelism - Use default
Maximum value for Node IDunless your graph contains exceptionally large IDs
- Keep
- Click Run.
- Preview results under the Data tab.

¶ Use Cases
- Social Network Analysis: Identify influencers and connectors in communication graphs.
- Fraud Detection: Spot nodes with abnormal connectivity or leadership roles.
- Graph Simplification: Use core numbers to focus on core components and filter noise.
- Academic Research: Understand core-periphery structures in citation or co-authorship networks.
- Community Ranking: Score and prioritize nodes within clustered communities.
- Notes:
- The action supports weighted graphs and provides more accurate core metrics in such scenarios.
- Leadership detection is binary (1 = leader, 0 = non-leader) and depends on structural patterns.
- The higher the
coreNumber_weighted, the more embedded and central the node is within the graph.
