¶ Description
Apply R-based predictive model.
¶ Parameters
¶ Parameters tab
Parameters:
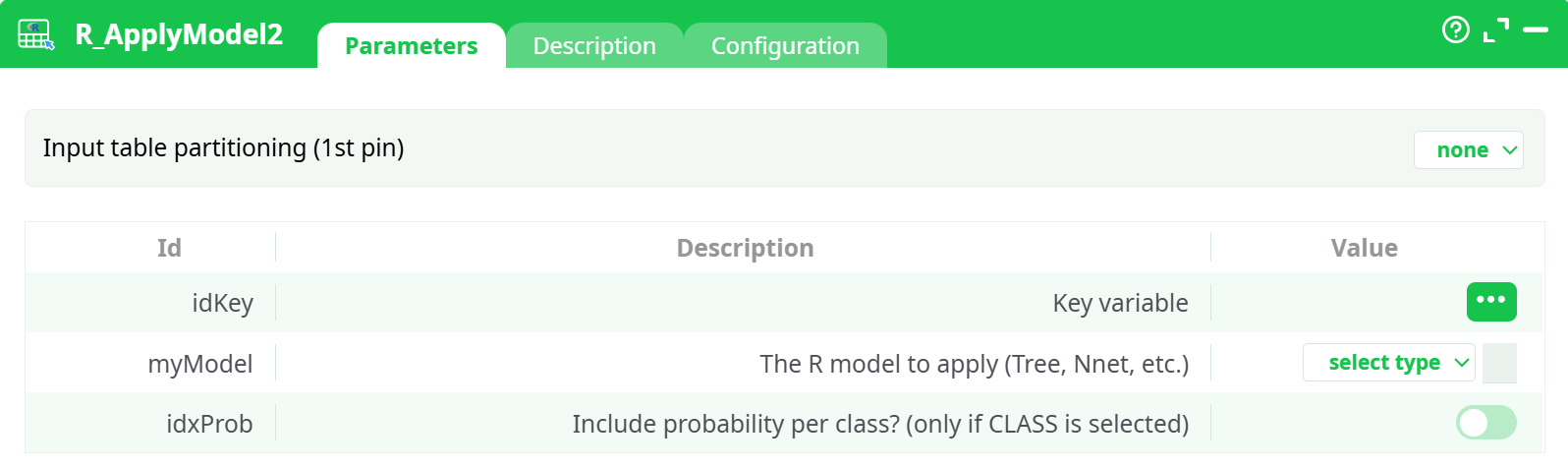
- Input table partitioning (1st pin)
- Number of lines
- Key variable
- The R model to apply (Tree, Nnet, etc.)
- Include probability per class? (only if CLASS is selected)
- Model names from input pin
¶ Description tab
Parameters:
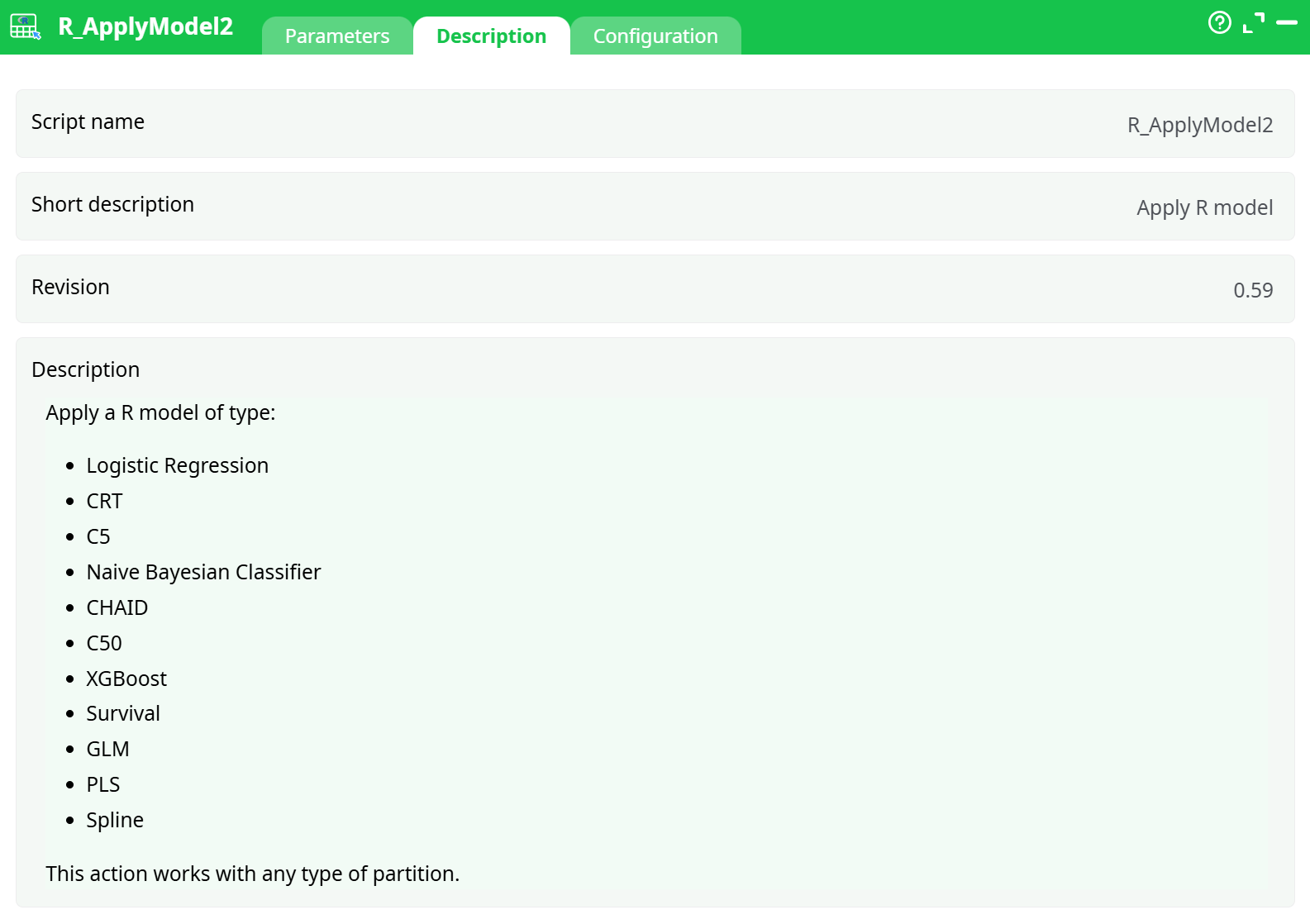
- Script name
- Short description
- Revision
- Decription
¶ Configuration tab
See dedicated page for more information.
¶ About
R_ApplyModel2 loads one or more previously trained R models and scores any input table—no matter how it’s partitioned. Because models are read from files rather than re-fit in memory, you can score datasets that are much larger than available RAM. The action also supports opening many models at once in a single run, which is ideal when you maintain a library of models (e.g., GLM, Logistic Regression, C5/C50, CHAID/CRT trees, Naïve Bayes, XGBoost, Survival, PLS/Splines, etc.).
Typical uses:
- Periodic batch scoring (daily/weekly inference)
- Back-testing several model candidates on the same dataset
- Productionizing models trained in other R actions (e.g., R_GLM, R_C50, R_XGBoost)
¶ Inputs & outputs
¶ Input (pin 1)
A table to score. Any partitioning is accepted (row, column, by-column, or none).
Requirements
- A unique identifier column (the Key variable).
- All predictor columns used by the model(s) must be present and of compatible types (names are matched case-sensitively).
¶ Output
The input rows plus the scoring results. Depending on the model type, columns may include:
*.Classor*.Response– predicted class/response*.Prob_<class>– class probabilities (optional; only if enabled and supported by the model)*.Score/*.Risk– numeric scores when applicableModelName– the name of the model file used (helpful when scoring multiple models)
(Exact column names vary by algorithm; R_ApplyModel2 keeps each model’s fields prefixed or suffixed to avoid clashes.)
¶ Parameters
| Parameter | What it is | Tips |
|---|---|---|
| idKey (Key variable) | The unique identifier column in your input table. | Pick the column you will join on (e.g., customer_id, row_id). |
| myModel (The R model to apply) | Where to load model files from. | Click the dropdown next to select type to choose: assets (bundled files), temporary data, recorded data (recommended; e.g., models produced earlier in the pipeline), JavaScript expression, or @shared source. Select one or many *.rModel files. |
| idxProb (Include probability per class?) | Adds per-class probabilities to the output when the model supports it. | Only meaningful for classification models (Logistic, Naïve Bayes, C5/C50, XGBoost-classifier, etc.). Leave off for regression models. |
📦 Model files
The training actions that create models (GLM,C50, XGBoost, etc.) typically emit*.rModel. Point myModel to these files (often via recorded data → records/out.rModel from the upstream training node).
¶ Quick start (minimal run)
-
Upstream: Train a model with one of the R training boxes and make sure it outputs a
*.rModelfile (default path is oftenrecords/out.rModel). -
Connect data: Feed the table you want to score into R_ApplyModel2 (pin 1).
-
Set parameters:
- idKey → choose your unique row id (e.g.,
row_id). - myModel → choose recorded data, then pick
records/out.rModelfrom the training node (you can pick multiple). - idxProb → turn ON if you want per-class probabilities (classification models only).
- idKey → choose your unique row id (e.g.,
-
Run.
The output table in Process → Data will show predictions (and probabilities if selected). You can also find the scored table under Records depending on your pipeline settings.
¶ Working with multiple models
- You can select several
*.rModelfiles at once. R_ApplyModel2 will apply each model across the full dataset and append the corresponding outputs. - Use the ModelName (or similar) column to disambiguate which model produced which set of scores.
- If you plan to compare models, keep consistent predictor names and datatypes across training and scoring.
¶ Best practices & tips
- Schema compatibility: The input must contain the same predictor names (and compatible types) as used during training. If you see errors about missing columns or factors with “new levels”, add preprocessing steps to align levels (e.g., map/merge rare categories to “Other”).
- Choose “recorded data” for models: This points directly to the output of the upstream training node and is the most robust way to wire models through the pipeline.
- Probabilities: Enabling idxProb increases the number of columns. Useful for calibration, uplift charts, threshold selection, and ROC/PR analysis.
- Large data: Because scoring loads models from files and streams rows, it scales well to tens/hundreds of millions of rows (bounded by your pipeline partitioning and storage throughput rather than RAM).
- Versioning: Keep model files under versioned names (e.g.,
churn_v2025_09_18.rModel) so you can reproduce runs and audits.
¶ Common errors & how to fix them
-
“Model not found” or cannot open connection
Ensure myModel points to an existing*.rModel(e.g., via recorded data → records/out.rModel). If the training node didn’t write the file, enable its model output. -
“Object … not found” or missing predictor columns
Add a prepare step to create/rename the missing columns to match training. -
“Factor has new levels …”
Your scoring data contains unseen categories. Reuse the same encoding/mapping used in training (e.g., collapse rare labels, ensure identical factor level ordering).
¶ Notes on supported algorithms
R_ApplyModel2 is model-agnostic and can apply models produced by many R actions, including (but not limited to):
- Logistic Regression / GLM
- CRT / CHAID / C50 decision trees
- Naïve Bayesian Classifier
- XGBoost (classification & regression)
- Survival models
- PLS / Splines
If an algorithm supports both class and probability outputs, idxProb gives you both the predicted class and per-class probability columns.