¶ Description
Slice a large graph into smaller graphs using MST algorithm.
¶ Parameters
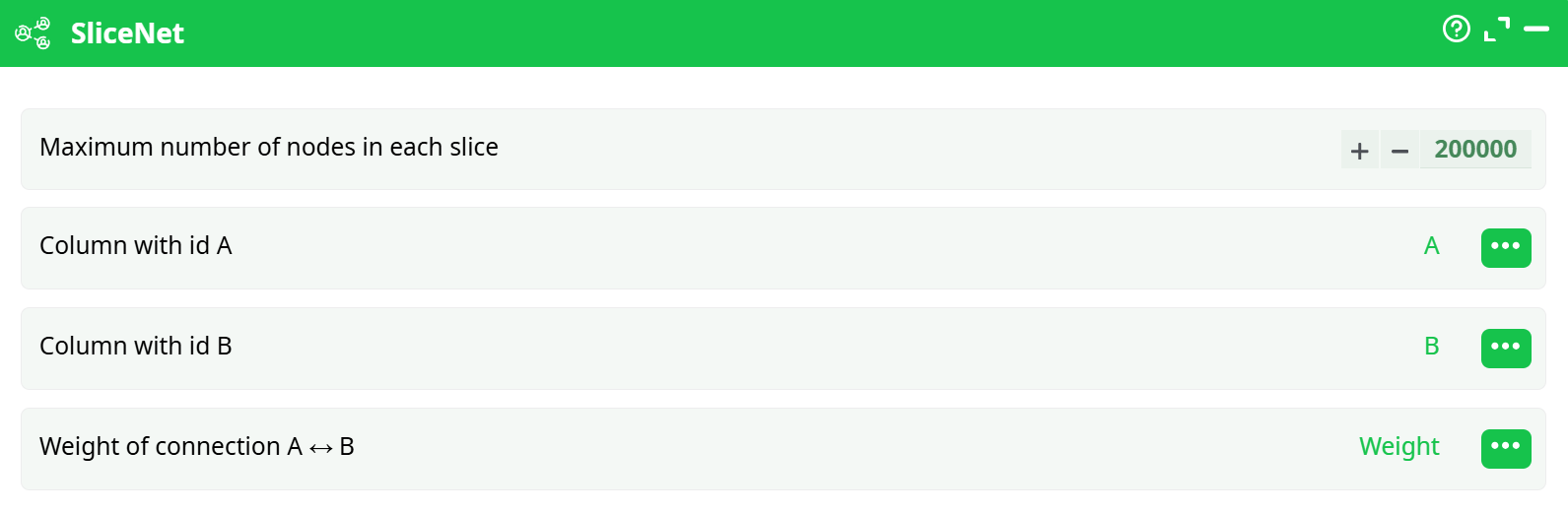
Parameters:
- Maximum number of nodes in each slice: The upper limit of nodes per slice. Used to control memory usage and slice granularity.
- Column with id A: The source node of the connection (from-node).
- Column with id B: The destination node of the connection (to-node).
- Weight of connection A<->B: Edge weight used to prioritize slicing. Must be sorted in descending order.
¶ About
The SliceNet action button is designed to partition large graphs into manageable subgraphs or "slices", each with a limited number of nodes. This is particularly useful for distributed processing, memory optimization, or parallel analysis in large-scale graph workflows. The slicing is based on edge weights and sorted connections, prioritizing stronger links between nodes.
¶ Use Cases
- Distributed Graph Processing: Breaks a massive network into smaller pieces for cluster execution.
- Batch Execution: When systems cannot handle the full graph at once, slices allow partial runs.
- Memory Management: Reduces the risk of memory overload by slicing graphs before intensive computations.
- Focused Analysis: Enables focused subgraph examination, ideal for community or region-based analysis.
¶ Important Requirements
Before running this action, ensure:
- The input table must be sorted by the weight column in numerical descending order.
- If not sorted correctly, an error will occur:
- ERROR: the input table must be sorted on the weight column using the 'number decreasing' sorting algorithm.
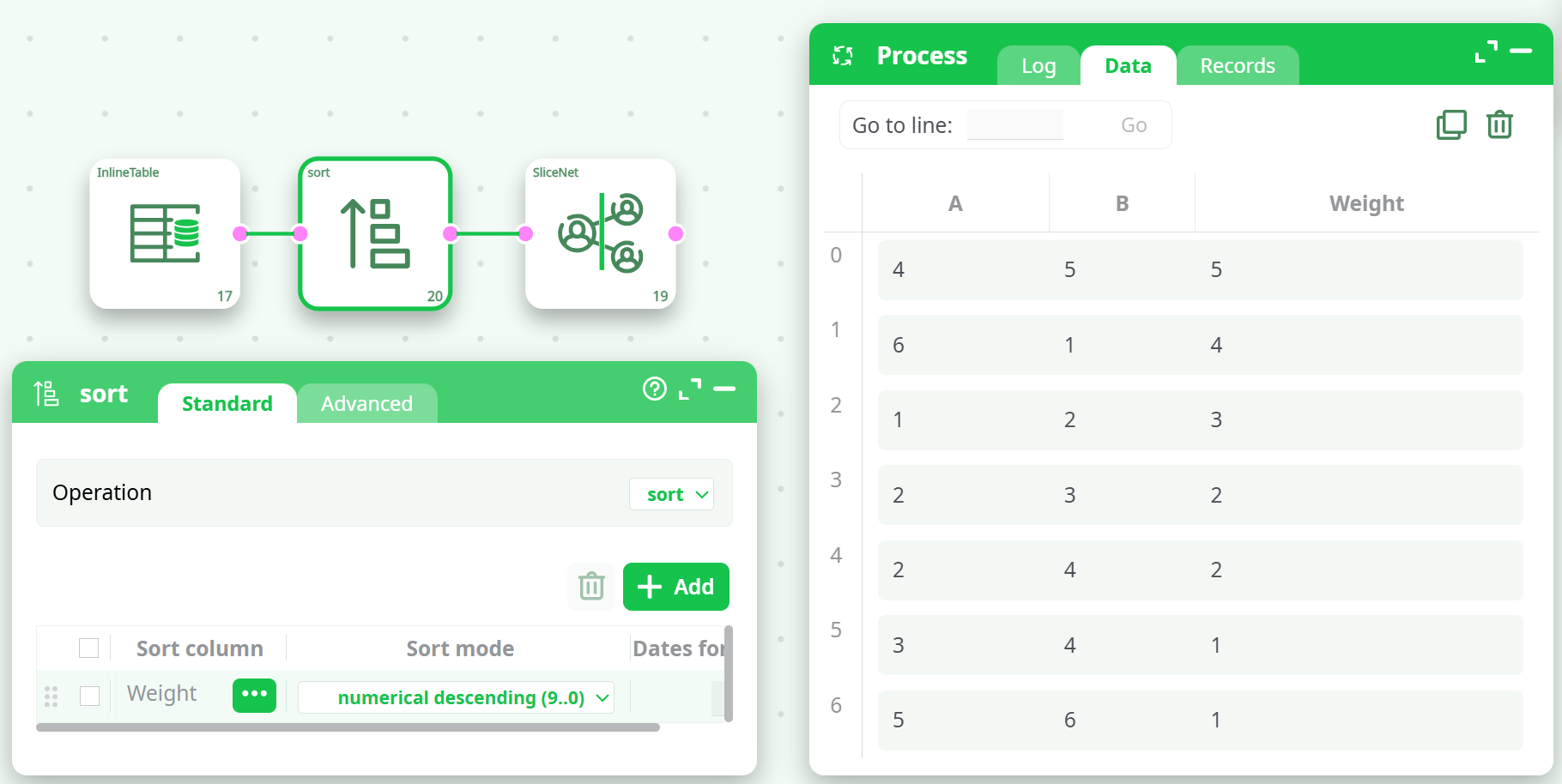
¶ Sorting Example
Use the Sort action before SliceNet:
- Sort by
Weight - Mode:
Numerical Descending
¶ How to Run
- Prepare Input Data
- Must include columns for source (A), destination (B), and weight.
- Sort Input
- Use the
Sortaction to sort byWeightin descending order.
- Configure Parameters
- Set the
Maximum number of nodes in each slice(e.g.,200000) - Select the correct columns for ID A, ID B, and weight.
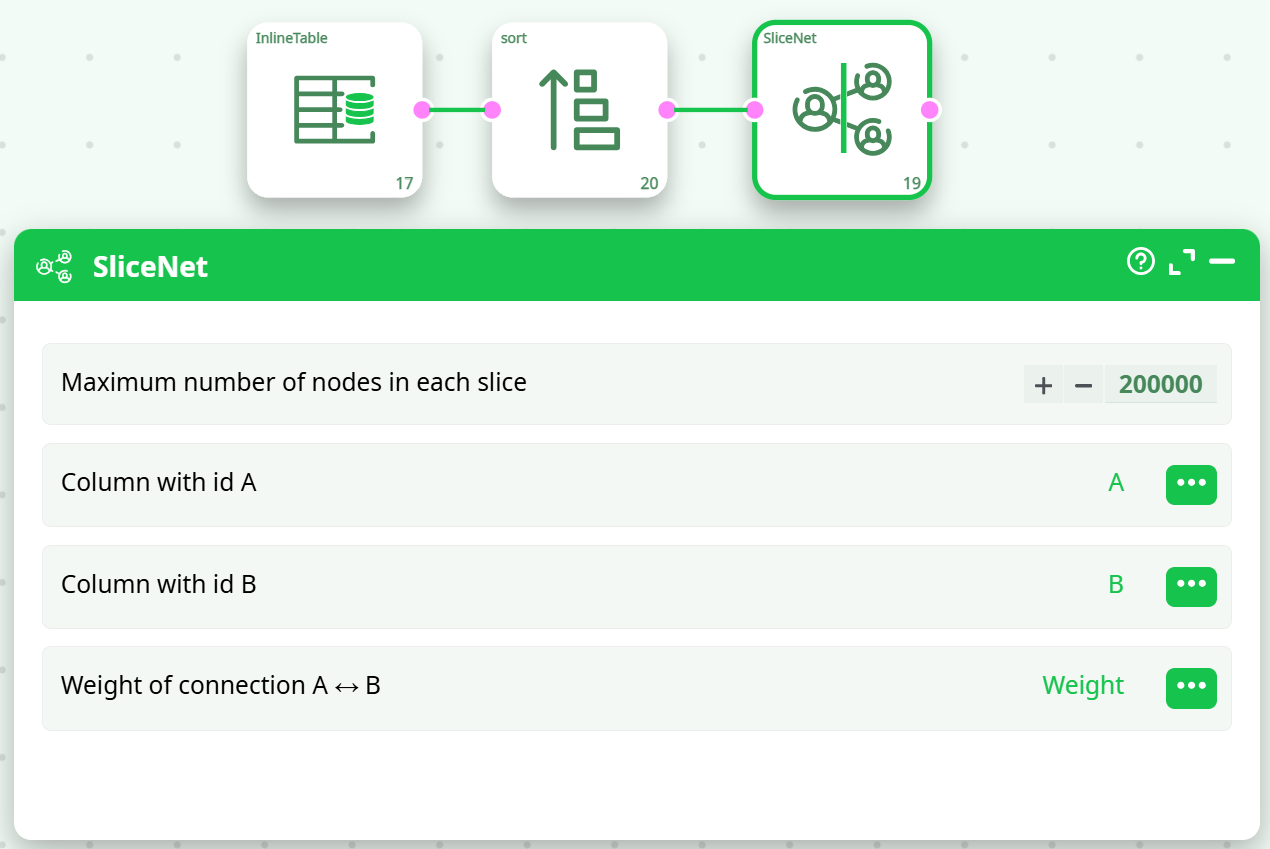
- Connect and Execute
- Link the output from the sort action to
SliceNet. - Execute the pipeline.
¶ Example Input
| A | B | Weight |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 2 | 3 | 2 |
| 3 | 4 | 1 |
| 4 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 6 | 1 |
| 6 | 1 | 4 |
| 2 | 4 | 2 |
¶ Notes
- For large graphs, reduce the slice size if memory issues occur.
- Ensure no duplicate or malformed edges exist.
- Combine with NodeAnalysis, Leadership, or Community Detection for enhanced workflows.
¶ Related Actions
- [Sort] – Prepares input for SliceNet.
- [NodeAnalysis] – Computes graph metrics post slicing.
- [Leadership] – Runs leadership ranking on sliced data.
¶ Final Tips
- Double-check sorting before connecting to SliceNet.
- Slice sizes can dramatically impact performance — test and adjust.
- If errors persist, export input data and test on a smaller subset.
