¶ Description
Geocode addresses using Bing.
¶ Parameters
¶ Parameters tab
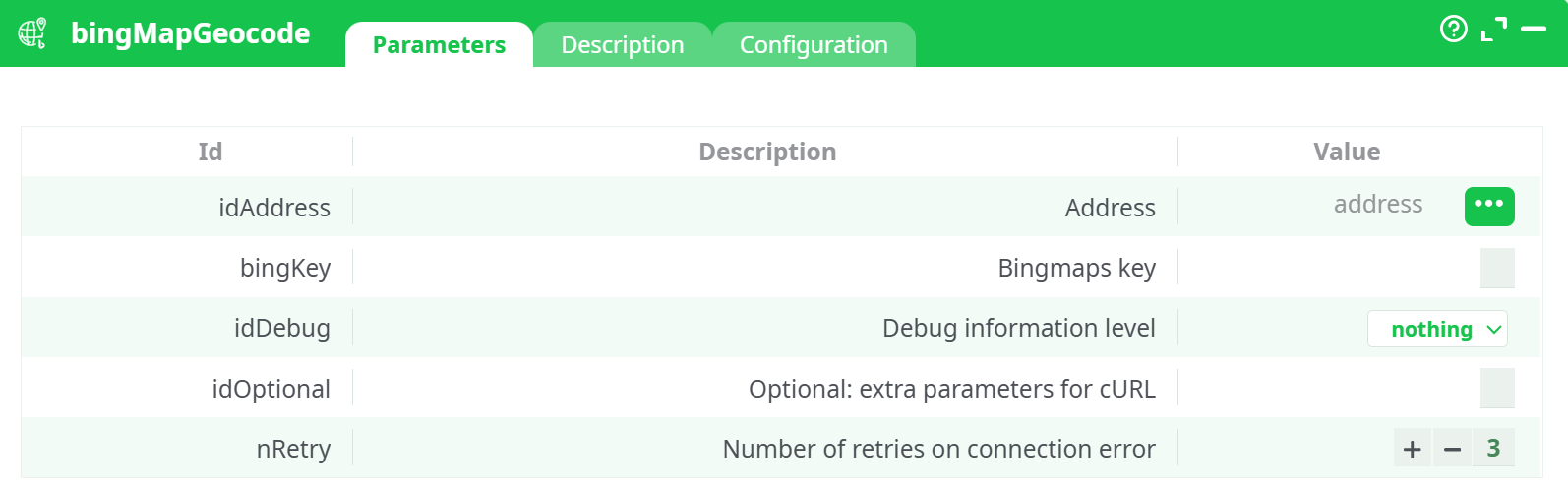
Parameters:
- Address
- Bingmaps key
- Debug information level
- Optional: extra parameters for cURL
- Number of retries on connection error
¶ Description tab
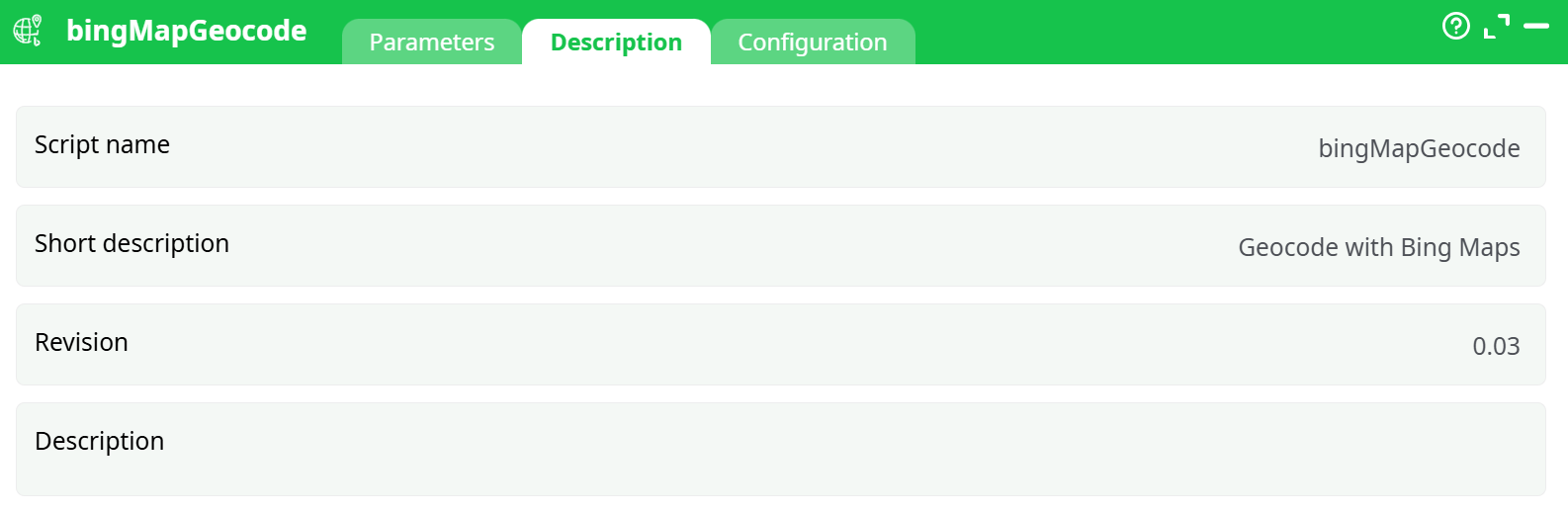
Parameters:
- Script name
- Short description
- Revision
- Description
¶ Configuration tab
See dedicated page for more information.
¶ About
This action also works when accessing the web through a PROXY server.
To use this action, you’ll first need to get a “BingMaps Key” from the Bing Maps website (parameter P2).
Once you have completed the “setup process”, you can use this action. This is pretty straightforward: Just give the column (in parameter P1) that contains some postal addresses “as-if” these addresses where written directly inside BING. Then, EL will give the following 16 columns in the output table:
Latitude, Longitude, Confidence, statusCode, statusDescription, authenticationResultCode, copyright, EstimatedTotal, AddressLine, AdminDistrict, AdminDistrict2, CountryRegion, FormattedAddress, Locality, PostalCode, MatchCode.
Each call to the BING engine is slow (because all internet-based REST api calls are always slow). So, you want to avoid to geocode 2 times the same address (to avoid losing time). To be sure to save all the geocoding results on the hard-drive as soon as they have been extracted from BING, you should use the writeSQLITE action with the option “Commit every 1 row” enabled:
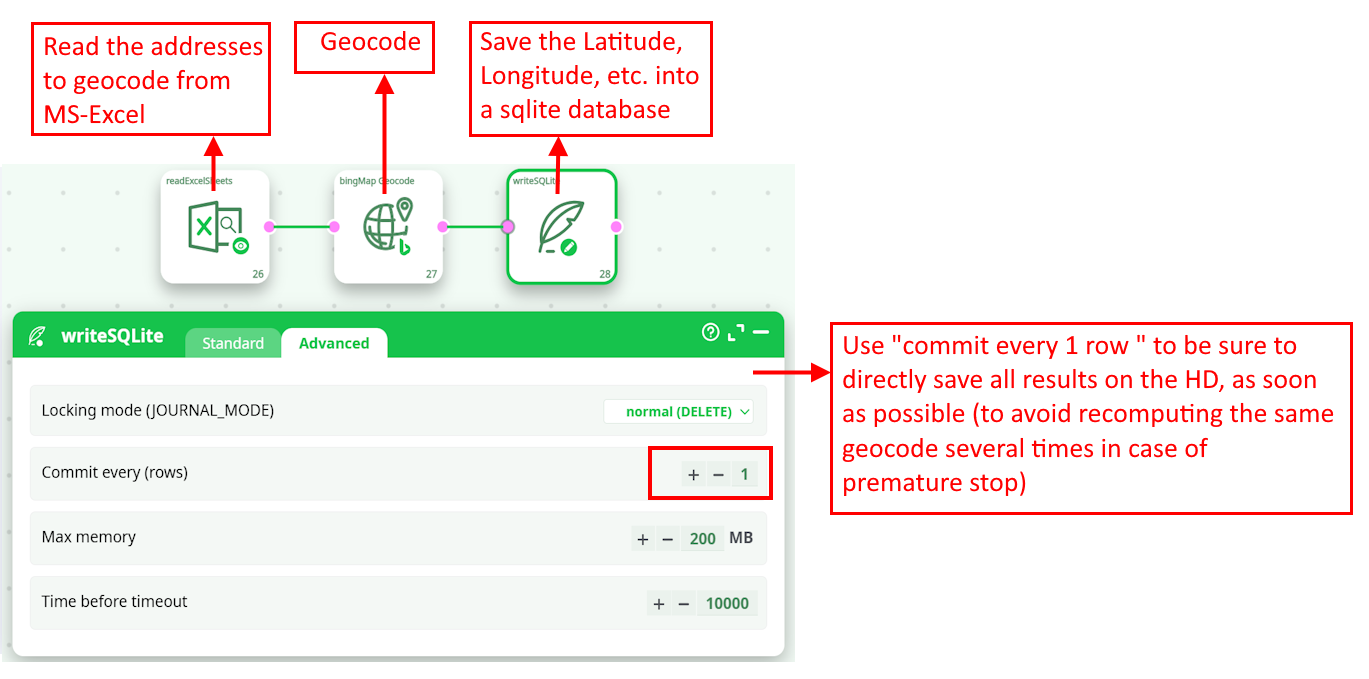
In the above pipeline, the addresses to geocode are directly extracted from an Excel file. Ideally, you should have a slightly more complex ETL pipeline that removes all the already-geocoded addresses (that are stored inside the SQLite file) from the input of the bingMapGeocode action (to avoid to geocode 2 times the same address).
¶ How to get you Bing Map Key
The procedure to get you Bing Map key is:
- Open the URL https://www.bingmapsportal.com and click the “sign-in” button:
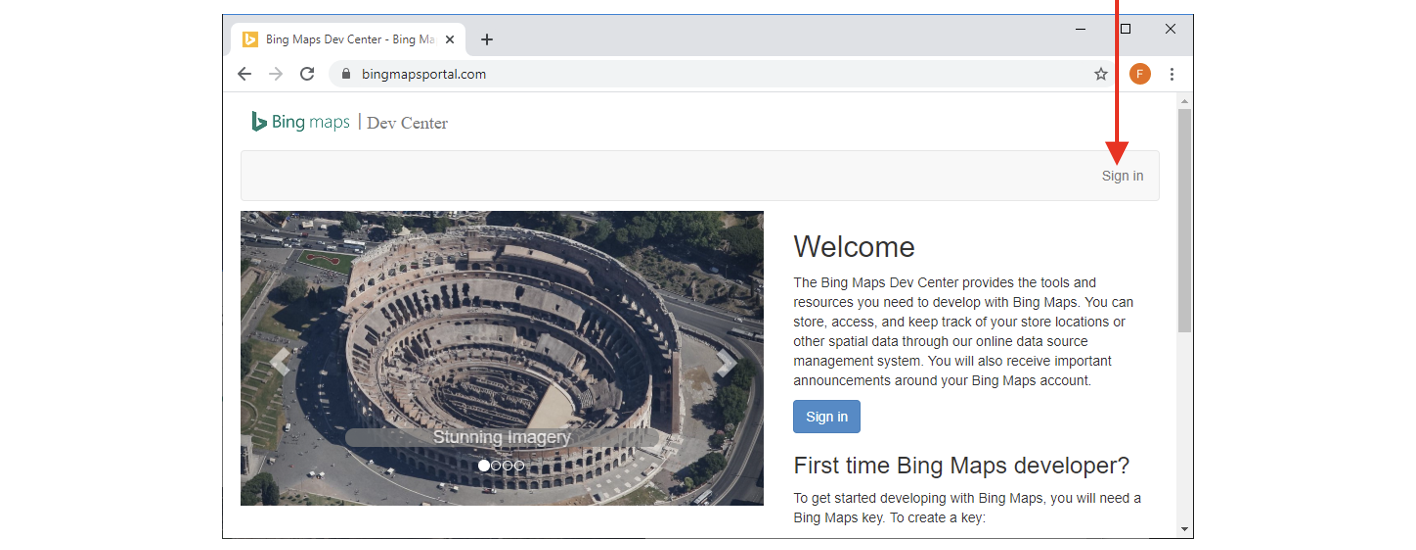
- Fill-in the form to create an account and click the “Create” button:
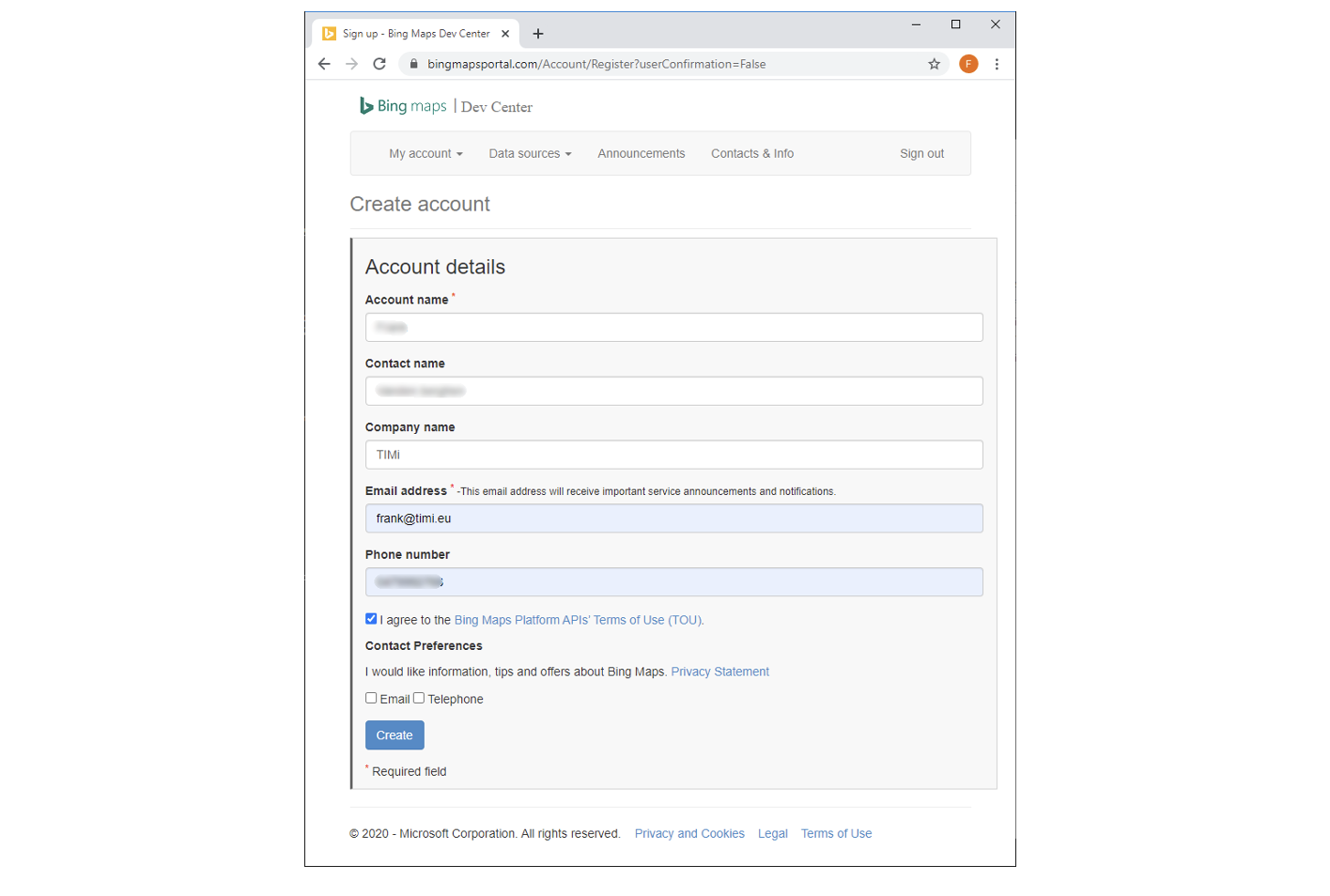
- Inside the Drop-Down menu “My account”, click on “My Keys”:
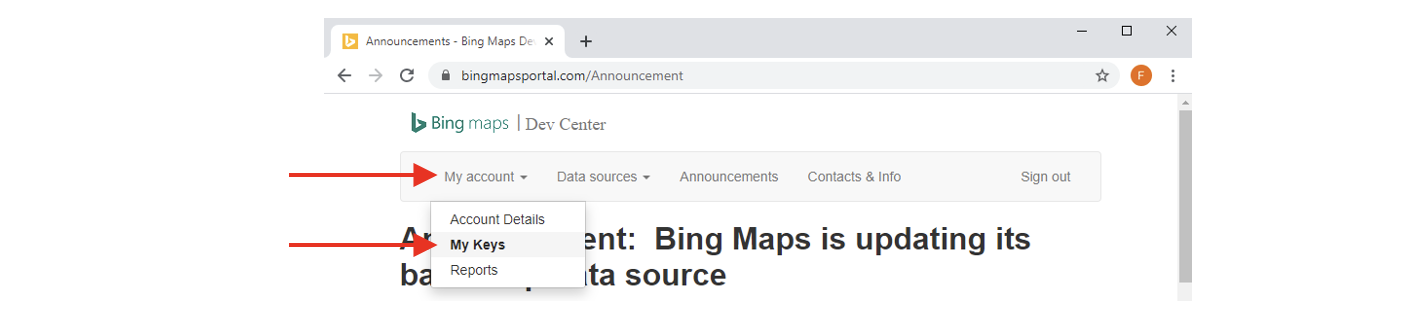
- Fill-In the form to get your key:
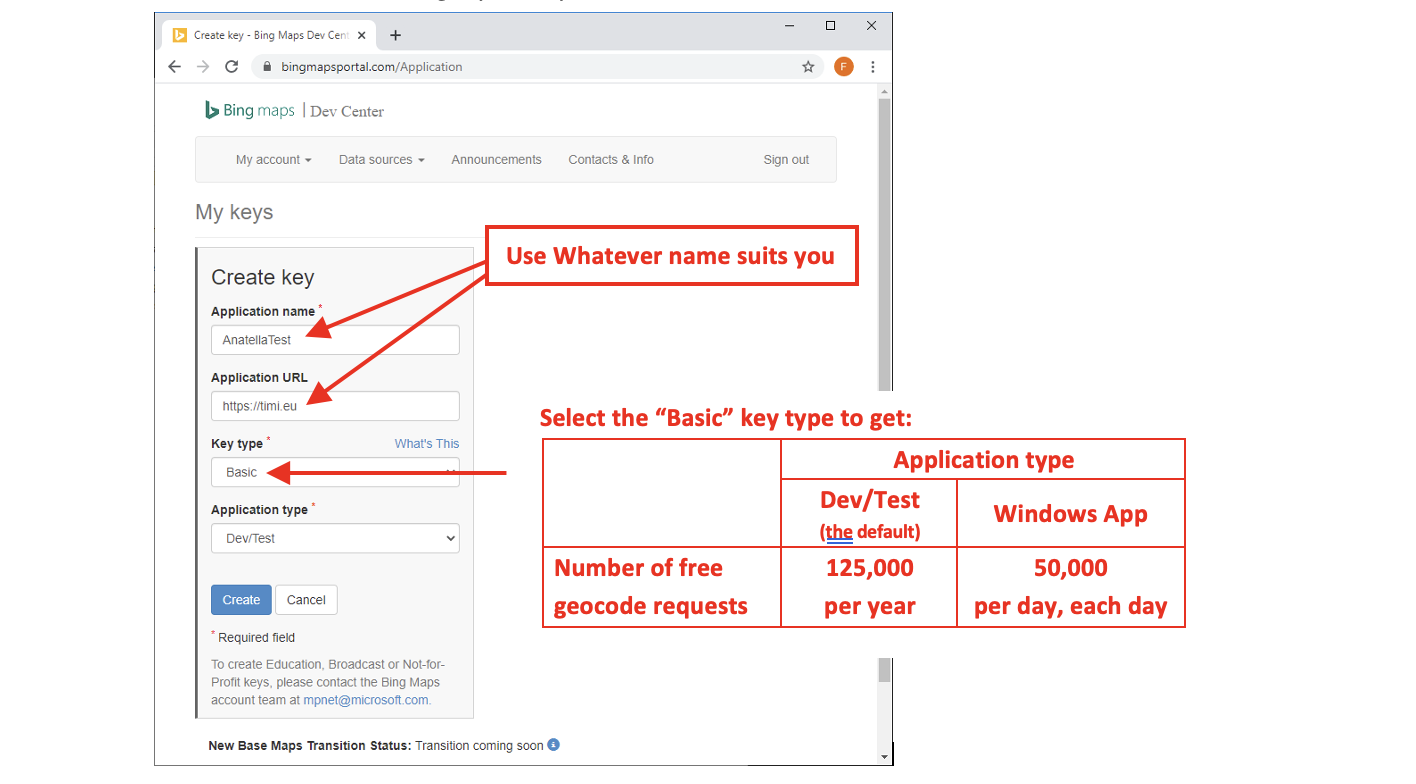
You’ll find more information about the different licensing options for Bing Maps here: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/maps/licensing/
Basically, if you need to make more geocoding requests than the limits detailed here, then you need to purchase an “Enterprise Key” (i.e. the “Basic” key is not enough).
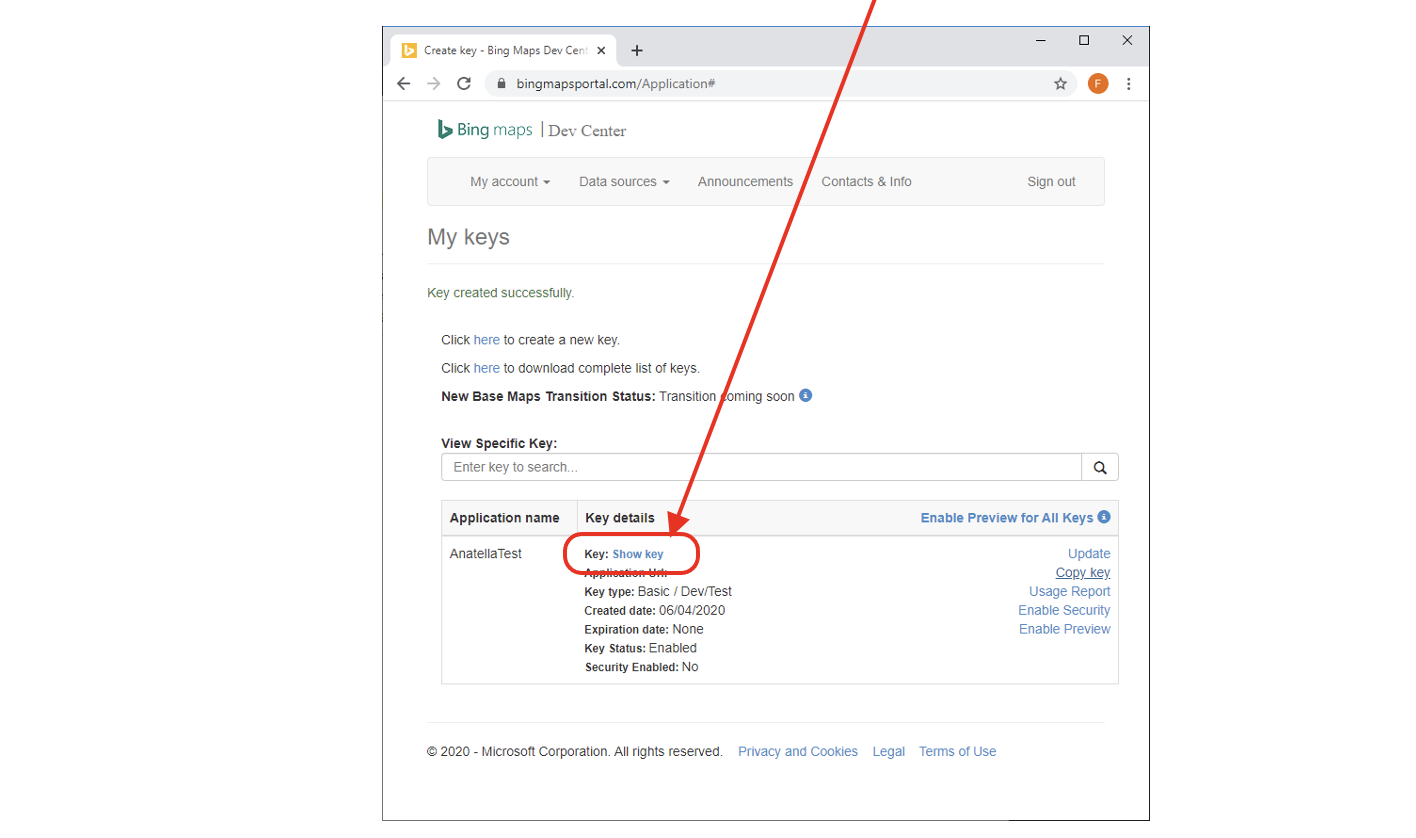
- You get your key: Click on the “show key” link to reveal it: