¶ Description
Upload Data to Microsoft Dynamics CRM
¶ Parameters
¶ Standard tab
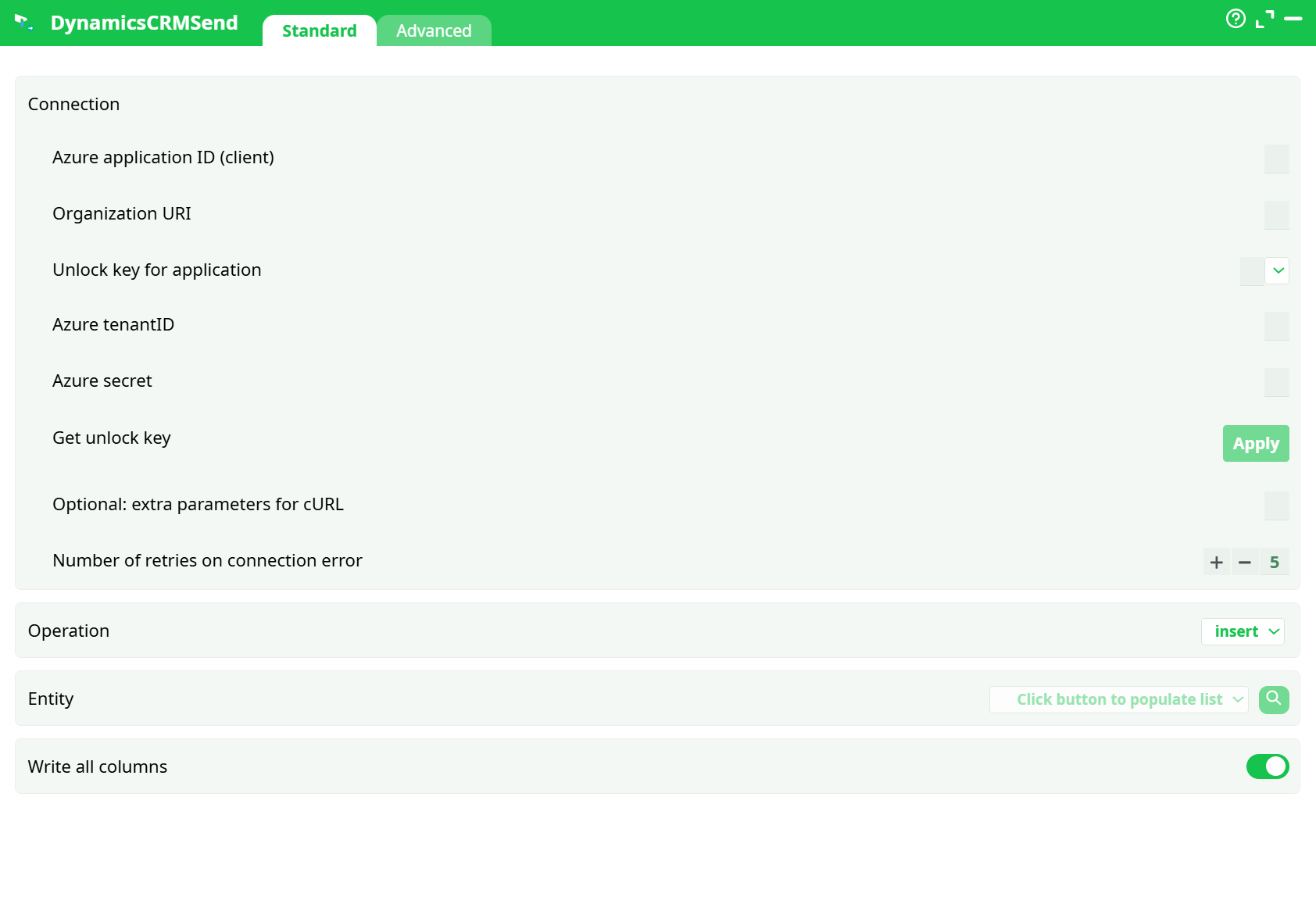
Parameters:
- Connection
- Azure application ID (client)
- Organization URI
- Unlock key for application
- Azure tenantID
- Azure secret
- Get unlock key
- Optional: extra parameters for cURL
- Number of retries on connection error
- Operation
- Entity
- Write all columns
¶ Advanced Tab
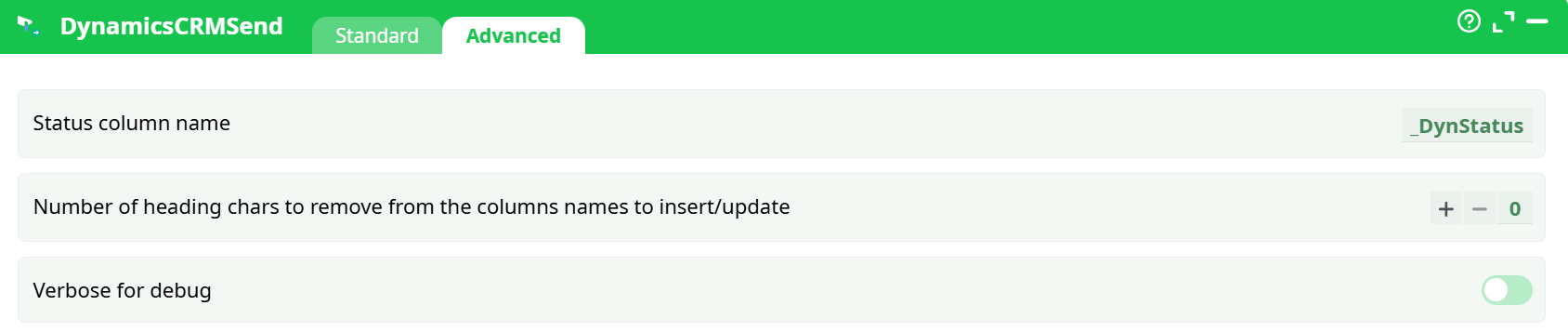
Parameters:
- Status column name
- Number of heading chars to remove from the columns names to insert/update
- Verbose for debug
¶ About
DynamicsCRMSend pushes records from your pipeline into Microsoft Dynamics 365 / Dataverse using the Web API. It supports insert, update, and delete operations against any standard or custom table (entity). The action reads a tabular dataset from its input pin and writes one record per row to the target entity, appending a per-row status column for auditability.
¶ Prerequisites
-
Dataverse environment (Organization URI such as
https://<org>.crm.dynamics.com). -
Azure AD app registration dedicated for Dataverse access:
-
Collect Application (client) ID, Directory (tenant) ID, and Client secret.
-
Grant the app appropriate Dataverse access:
- Delegated: add Dynamics CRM – user_impersonation and approve consent; or
- Application user: create an Application User in the environment and assign a security role that permits create/update/delete on the target tables.
-
-
AzureUnlock set up in this pipeline (or another pipeline) so this action can reuse OAuth tokens:
- You’ll reference the unlock key (a pipeline constant, for example
azunlock-<org>-dynamics-v1>), or click Get unlock key in the action to add it automatically.
- You’ll reference the unlock key (a pipeline constant, for example
-
Table(s) and attributes exist in Dataverse, with primary keys/alternate keys configured for update/delete operations.
-
The upstream action provides a dataset whose column names match the Dataverse logical attribute names (see Input Requirements).
¶ Input Requirements
-
Single tabular input. Each row represents one record to send.
-
Column naming:
-
For insert, include all required attributes for the target entity plus any optional attributes you want to set. Column names must be the logical names (e.g.,
firstname,lastname,emailaddress1). -
For update:
- Provide the primary key column (logical name
<entity>id, e.g.,contactid) or a configured alternate key column(s). - Only the provided columns are updated.
- Provide the primary key column (logical name
-
For delete, provide only the primary key (or alternate key) column(s).
-
-
Lookups: supply the GUID of the referenced record (as a string) in the lookup attribute’s logical name; for polymorphic lookups, use the correct attribute.
-
Choice/Status: send the integer option values (not labels).
-
Date/Time: send ISO-8601 strings in UTC, unless your org/table expects a different behavior.
-
Large text: ensure values are within Dataverse limits for the target attribute type.
Parameter interdependencies
- Unlock key for application requires that Azure application ID, Azure secret, Azure tenantID, and Organization URI align with the same Azure app & environment used by AzureUnlock.
- Operation = update/delete requires a resolvable key (primary GUID or alternate key columns) in each row; otherwise the row fails with 400/404.
- Write all columns = true sends every matching attribute; set to false if you pass convenience columns you do not want written.
¶ Example Workflow (step-by-step)
- Prepare connection
Add Azure application ID (client), Organization URI, Azure tenantID, and Azure secret.
Click Get unlock key to create/populate the unlock constant (or paste your existing key). - Choose operation & entity
Set Operation toinsert,update, ordelete. Click the Entity picker to fetch the list and select the entity logical name. - Map columns
Ensure your upstream dataset’s columns are logical attribute names. If your columns have a prefix, set Number of heading chars to remove accordingly. Toggle Write all columns as desired. - Tune reliability
Leave Number of retries at5(good default). Only add extra cURL parameters if your network/proxy requires it. - Run
Execute the pipeline. Check the status column and the Log tab for per-row results and any API messages. - Validate
In Dataverse (Advanced Find/Modern Advanced Filters or table view), confirm records and a sample of updated fields. For deletes, verify recycle bin/audit if enabled.
¶ Troubleshooting
401 UnauthorizedorAuthorization required, but no authorization protocol specified
Wrong unlock key, expired/missing client secret, or AzureUnlock not executed. Re-create the unlock key and verify tenant/app/secret values.403 Forbidden
App user lacks privileges for the entity/table. Assign/adjust Dataverse security role to include create/update/delete.404 Not Found
Entity logical name incorrect, or key does not resolve (bad GUID/alternate key mismatch).400 Bad Request
Attribute name not valid for the entity, data type mismatch (e.g., sending text to a numeric field), option set expects integer value, or lookup needs a valid GUID.- Concurrency errors (412 Precondition Failed)
If your environment enforces row version checks, include the correct ETag/rowversion or avoid conditional updates. - Throttling (429) / 5xx
Increase Number of retries, add backoff in the pipeline, and reduce batch sizes upstream if applicable. - Lookup/Relationship issues
Make sure you send the GUID of the related record. For polymorphic lookups, confirm the attribute accepts that type.
¶ Use Cases
- Bulk inserts of contacts/accounts/opportunities from staging tables.
- Field updates to synchronize attributes from a master source (e.g., marketing platform → Dataverse).
- Programmatic deletes to clean stale or duplicate data while maintaining an audit trail.
- Controlled writes from curated datasets where only whitelisted columns are pushed.