¶ Description
Upload file(s) to a remote Tableau Server.
¶ Parameters
¶ Parameters tab
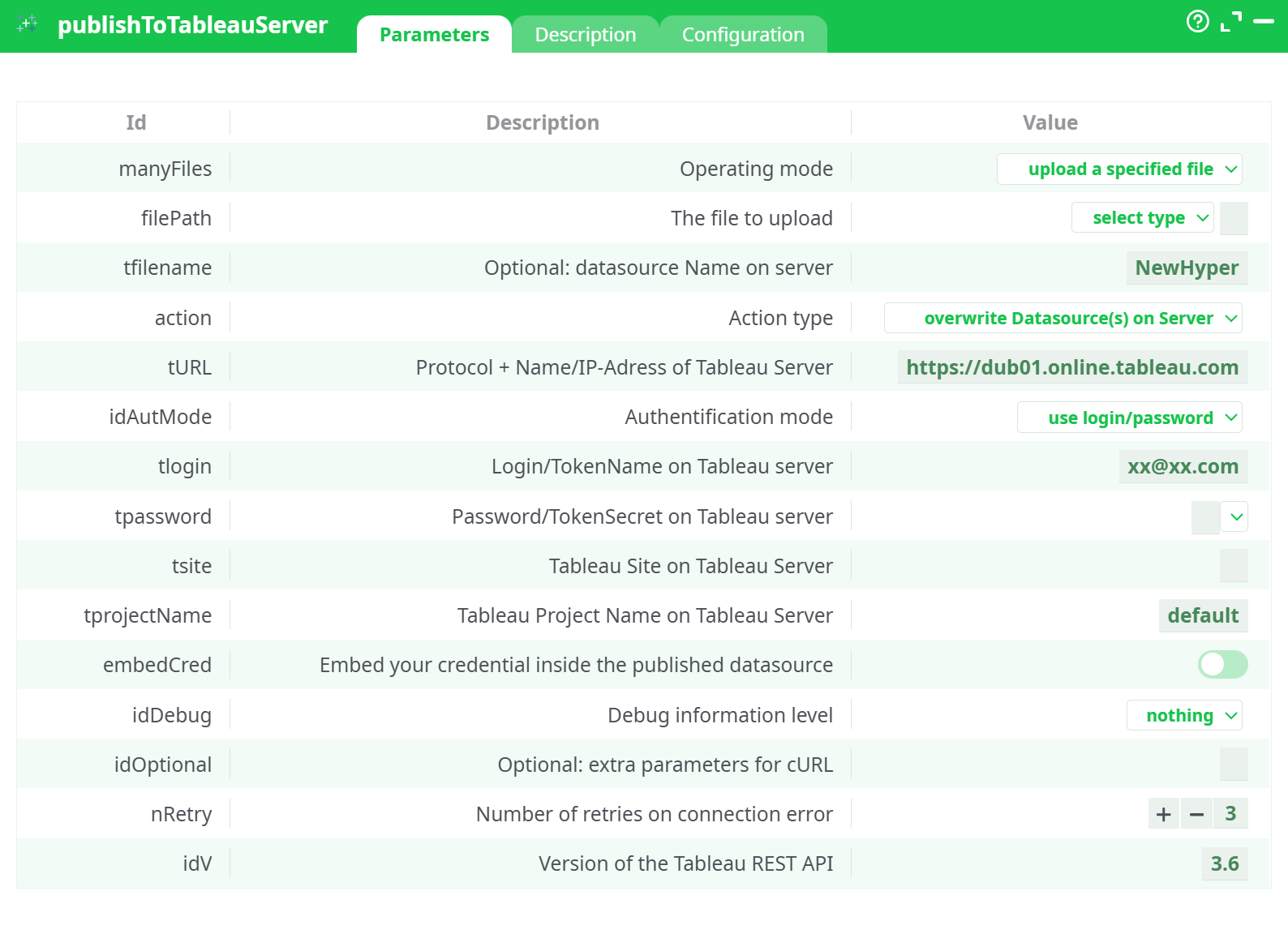
Parameters:
- Operating mode:
- The file to upload
- Optional: datasource Name on server
- Action type
- Protocol + Name/IP-Adress of Tableau Server
- Authentification mode
- Login/TokenName on Tableau server
- Password/TokenSecret on Tableau server
- Tableau Site on Tableau Server
- Tableau Project Name on Tableau Server
- Embed your credential inside the published datasource
- Debug information level
- Optional: extra parameters for cURL
- Retries on connection error
¶ Description tab
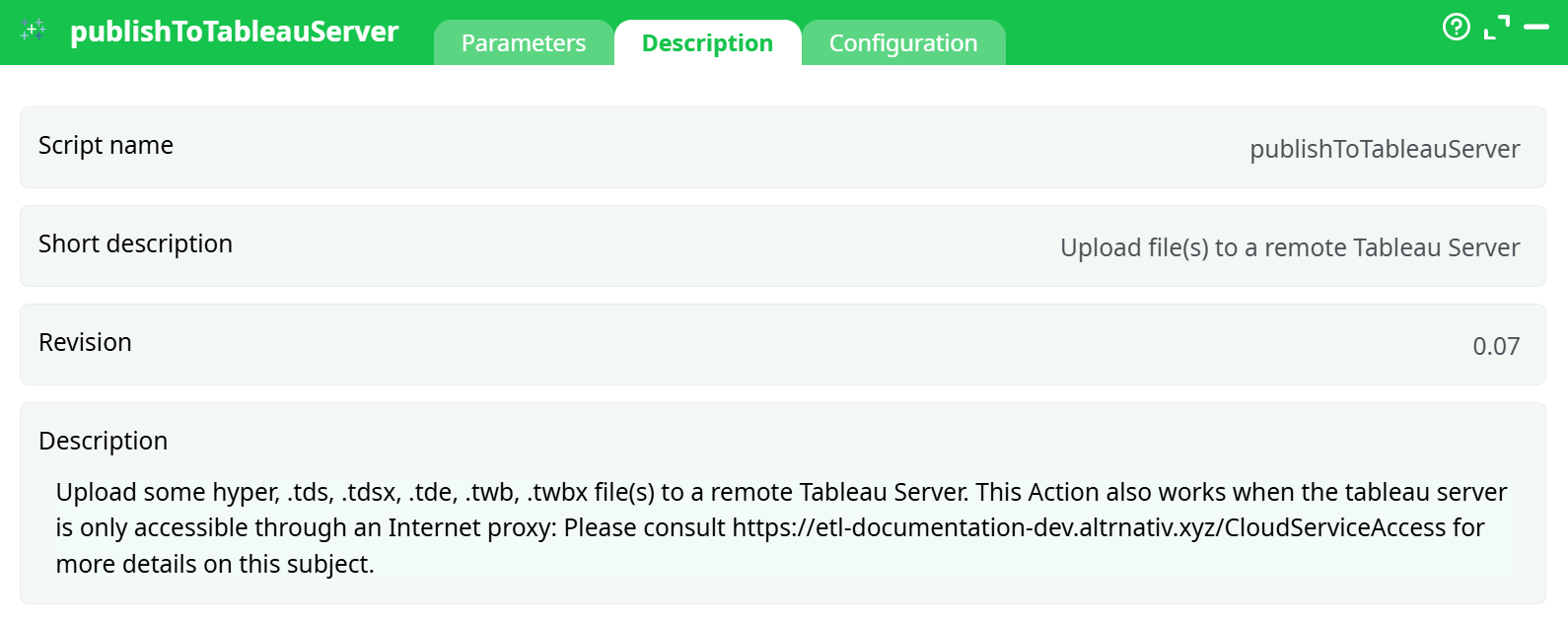
Parameters:
- Script name
- Short description
- Revision
- Decription
¶ Configuration tab
See dedicated page for more information.
¶ About
Uploads Tableau files to a remote Tableau Server or Tableau Cloud. Supported file types include:
.hyper,.tde,.ttde.tds,.tdsx.twb,.twbx
It works in environments that must access Tableau through an Internet proxy (see your platform’s “Cloud/Proxy access” notes).
¶ Typical workflow
- Use writeHyper (or another step) to produce a
.hyper/.tdelocally. - Use publishToTableauServer to upload that file to the target Site/Project so dashboards stay on “fresh & updated” data.
¶ Operating modes
- Upload a specified file
Choose one file from Assets / temp data / recorded data / disk image. - Upload all files specified in the input table
Feed the action with a table listing files to publish (one path per row); the action iterates and publishes each file.
¶ Authentication options
¶ Login/Password
- Provide tlogin (username) and tpassword (password).
- Use when traditional credentials are allowed.
¶ Personal Access Token (PAT)
- Set idAutMode to use Personal Access Token (PAT).
- tlogin = PAT Name, tpassword = PAT Secret.
- Preferred for Tableau Cloud and modern security practices.
¶ File selection (single-file mode)
Click filePath → select type, then pick from:
- Assets (packaged with the pipeline)
- temporary data (produced earlier in the flow)
- recorded data
- JavaScript expression (compute a dynamic path)
- Disk images (
@sharedmounts)
¶ Using bulk mode (many files)
- Switch manyFiles to upload all files specified in the input table.
- Provide an input table with one column containing file paths (and optional columns for per-row overrides like
tfilename). - The action publishes each row’s file in sequence and reports per-file status in the log.
¶ Common setups
¶ A) Publish a single .hyper and overwrite if it exists
- manyFiles:
upload a specified file - filePath: select your
.hyper - tfilename:
Sales_Weekly - action:
overwrite Datasource(s) on Server - tURL: your server URL
- idAutMode:
use Personal Access Token (PAT) - tlogin / tpassword: PAT Name / Secret
- tsite:
default - tprojectName:
Executive Dashboards - embedCred: on (so scheduled refresh works)
- nRetry:
3
¶ B) Append new data to an existing datasource
- Same as above but set action to
append to Datasource(s) on Server. - Ensure the schema matches the target datasource.
¶ C) Publish many files from a table
- manyFiles:
upload all files specified in the input table - Upstream step provides a table of file paths; optionally include columns for
tfilename,tprojectName, etc., if you want row-specific names/targets. - The action supports corporate proxies. Configure proxy/cURL options as needed using idOptional, or use your platform’s global proxy settings.
¶ Output & logging
- The action logs REST calls and server responses.
- Increase idDebug to
basicorverbosefor troubleshooting. - On failures, the step returns a non-zero status; nRetry covers transient network errors.
¶ Permissions & prerequisites
- The user (or PAT) must have permission to Publish to the chosen Site/Project.
- Ensure the Tableau REST API version (idV) is compatible with your server.
- For embedded credentials, the account you supply should have access to the underlying data sources.
¶ Troubleshooting
| Symptom | Likely cause | Fix |
|---|---|---|
| 401 Unauthorized | Bad credentials / PAT expired | Re-issue PAT or verify username/password |
| 403 Forbidden | No publish rights to Site/Project | Grant publish permission or switch Project |
| 409 Conflict on append | Schema mismatch | Align fields and types with the existing datasource |
| Timeout / SSL errors | Network/proxy/TLS issues | Add flags in idOptional (e.g., --connect-timeout 60), verify proxy/CA |
| Datasource visible but blank | Uploaded file empty or filtered upstream | Inspect upstream step and file content |
¶ Best practices
- Prefer PAT over username/password.
- Use embedCred for scheduled refreshes.
- Keep idV aligned with your server’s REST API level.
- Start with basic debug when validating a new connection; switch to nothing in production.
- Use append only when your schema is stable; otherwise overwrite to avoid polluted models.
