¶ Description
writeSASXPT exports the incoming table to a SAS XPORT (XPT v5) file. It can create a new .xpt file or append a dataset to an existing .xpt.
¶ Parameters
¶ Standard Tab
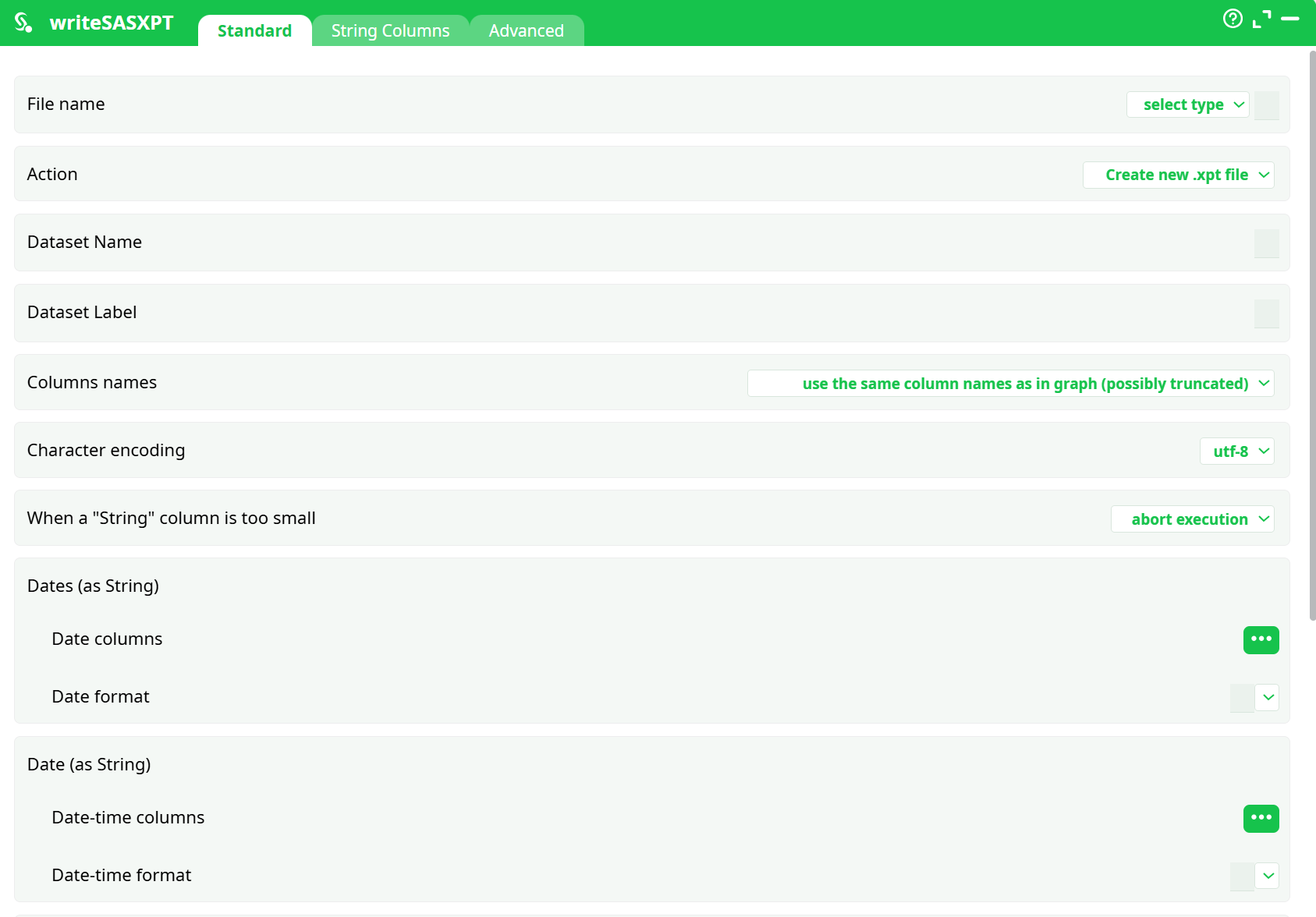
Parameters:
-
File name
-
Action
-
Dataset Name
-
Dataset Label
-
Columns names
-
Character encoding
-
When a "String" column is too small
-
Dates (as String)
- Date columns
- Date format
-
Date (as String)
- Date-time columns
- Date-time format
-
Date (as Elapsed-Time)
- Elapsed-Time date columns
- Elapsed time unit
- Reference date
-
Date-times (as Elapsed-Time)
- Elapsed-Time date-time columns
- Elapsed time unit
- Reference date
¶ String Columns Tab

Parameters:
- Suggested length of text field = max(observed_length,1) x security_factor_f1 + security_factor_f2
- Compute new "Observed length" for all strings
- Use all "Observed length" as "Final length"
¶ Advanced Tab
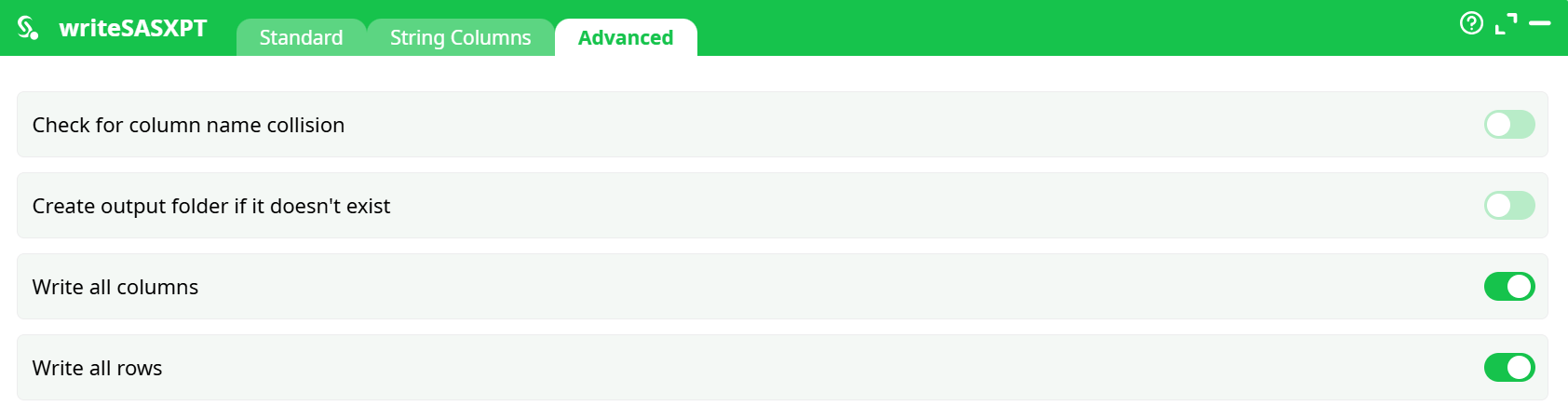
Parameters:
- Check column name collisions
- Create output folder if it doesn't exist
- WWrite all columns
- Write all rows
¶ About
writeSASXPT exports the incoming table to a SAS XPORT (XPT v5) file. It can create a new .xpt file or append a dataset to an existing .xpt. It also lets you:
- control dataset name/label,
- normalize string column lengths (avoid truncation),
- define date/datetime conversions from strings or elapsed-time fields,
- choose character encoding.
Typical use cases:
- Delivering clinical/biostatistics datasets to systems that accept SAS XPT v5 only.
- Packaging multiple datasets into a single
.xptfor exchange. - Producing a portable archive from a pipeline for downstream SAS users.
¶ Quick Start (minimal config)
-
Upstream input: connect a table (e.g., from
readCSV). -
Open writeSASXPT → Standard:
- File name:
records/out.xpt(or any path; your screenshots userecords/out.xpt)
(You may also bind to a pin; keep it simple for quick tests.) - Action:
Create new .xpt file - Dataset Name:
DEMO - Dataset Label (optional): leave blank or short description
- Columns names:
use the same column names as in graph (possibly truncated) - Character encoding:
utf-8 - When a "String" column is too small:
truncate with warnings(safer first run)
- File name:
-
Run the graph.
Result: a file likeout.xptshown under Process → Records (click Download).
¶ Step-by-step run recipes
¶ Minimal export (no dates)
-
readCSV
- Input file:
assets/xpt_demo_min.csv - Delimiter
,, Header ON
- Input file:
-
writeSASXPT → Standard
- File name:
records/out.xpt - Action:
Create new .xpt file - Dataset Name:
DEMO - Columns names:
use the same column names as in graph (possibly truncated) - Character encoding:
utf-8 - When a "String" column is too small:
truncate with warnings
- File name:
-
Run → Download
out.xptfrom Process → Records.
¶ Parameter reference (what to set & when)
¶ Standard tab
-
File name
Path for the.xpt. Use a pin binding or a literal path, e.g.records/out.xptorassets/out.xpt. -
Action
Create new .xpt file— start a new container.Append to .xpt file— add a new dataset to an existing XPT (mind 8-char dataset name rule).
-
Dataset Name
≤ 8 chars, uppercase, no spaces (e.g.,DM,AE,DEMO,ORDERS). -
Dataset Label
Optional, ≤ 40 chars. -
Columns names
use the same column names as in graph (possibly truncated)— convenient; be aware of XPT limits.use the same column names as in graph (abort if truncation)— safer for regulated workflows.column names are C1, C2, … and column labels are ETL column names— use auto short names, keep human-friendly labels.
-
Character encoding:
utf-8(recommended) orLatin1. -
When a "String" column is too small
abort execution— strict; fails fast.truncate with warnings— practical for exploration; review warnings.
-
Dates (as String) / Date (as String)
Map string columns to SAS date/datetime by specifying columns and format masks (e.g.,yyyy-MM-dd,yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss). -
Date(s) as Elapsed-Time
If your date/time are numeric elapsed units since a Reference date (e.g., seconds since1970-01-01 00:00:00), specify:- Elapsed-Time columns
- Elapsed time unit (
second,minute,hour,day,week) - Reference date
¶ String Columns tab
Use to pre-size text fields and avoid truncation:
- Scan sample rows to compute observed length.
- Apply f1/f2 safety factors.
- Choose “Compute new Observed length for all strings” and/or “Use all Observed length as Final length”.
¶ Advanced tab
- Check column name collision — warns if duplicate names occur after truncation.
- Create output folder if it doesn’t exist — auto-create path.
- Write all columns / Write all rows — usually keep ON.
¶ Appending multiple datasets into one XPT
-
First action: set Action =
Create new .xpt file, Dataset Name =DM. -
Duplicate the action for a second input (e.g., AE) and set:
- Action =
Append to .xpt file - File name = same path (e.g.,
records/out.xpt) - Dataset Name =
AE
- Action =
-
Run both in sequence. The same
.xptwill contain datasets DM and AE.
¶ Troubleshooting
-
“Abort due to truncation / too-small string”
- Switch to
String Columnstab and increase lengths (via f1/f2 or set explicit max length). - Or change When a "String" column is too small →
truncate with warningsfor a trial run.
- Switch to
-
“XPT name violations”
- Ensure dataset/variable names ≤ 8 chars. Add a rename step before export or use the C1, C2, … option with labels.
-
File not created / path error
- Turn on Create output folder if it doesn’t exist (Advanced).
- Confirm the destination path (e.g.,
records/exists or auto-creation is enabled).
¶ Output location
After a successful run, download the XPT from: Process → Records → out.xpt.
If you used a different name or folder, it will appear under that path.