¶ Description
Propagate a cell to empty cells below.
¶ Parameters

Parameters:
-
Propagation rule
copy previous cell to empty or NULL cells: Fill all empty or NULL cells by copying the value from the previous row.copy previous cell to NULL cells: Only fill NULL cells, leaving empty strings untouched.
-
Output mode
update existing columns: Replaces values in the original column.create new columns: Generates a new column with propagated values, preserving the original data.
-
Columns to share
Select one or more columns in which propagation will be applied. -
Optional: partition column
Define a partitioning column so that the propagation is performed independently within each group. (e.g., reset at the start of each group) -
Check sort flag on partition column
Ensures the partition column is sorted before propagation. Enabling this is critical for consistent and logical filling within groups.
¶ About
The PropagateDown action is used to fill empty or NULL cells in a column by propagating values downward from previous rows. It is especially useful for forward-filling grouped or hierarchical data.
The PropagateDown action is commonly used when working with datasets where some rows are missing values in hierarchical or grouped data. For example, in reporting pipelines, a dataset might include a column with dates or category labels that only appear once per group, with subsequent rows left blank. To ensure data completeness and facilitate accurate joins, filters, or aggregations, the PropagateDown step fills these empty or NULL cells by copying the last known value downward within a column.
¶ Output
- When using update existing columns, the original column is directly modified.
- When using create new columns, the new column is named by appending an underscore (
_) to the original column name.
¶ Example
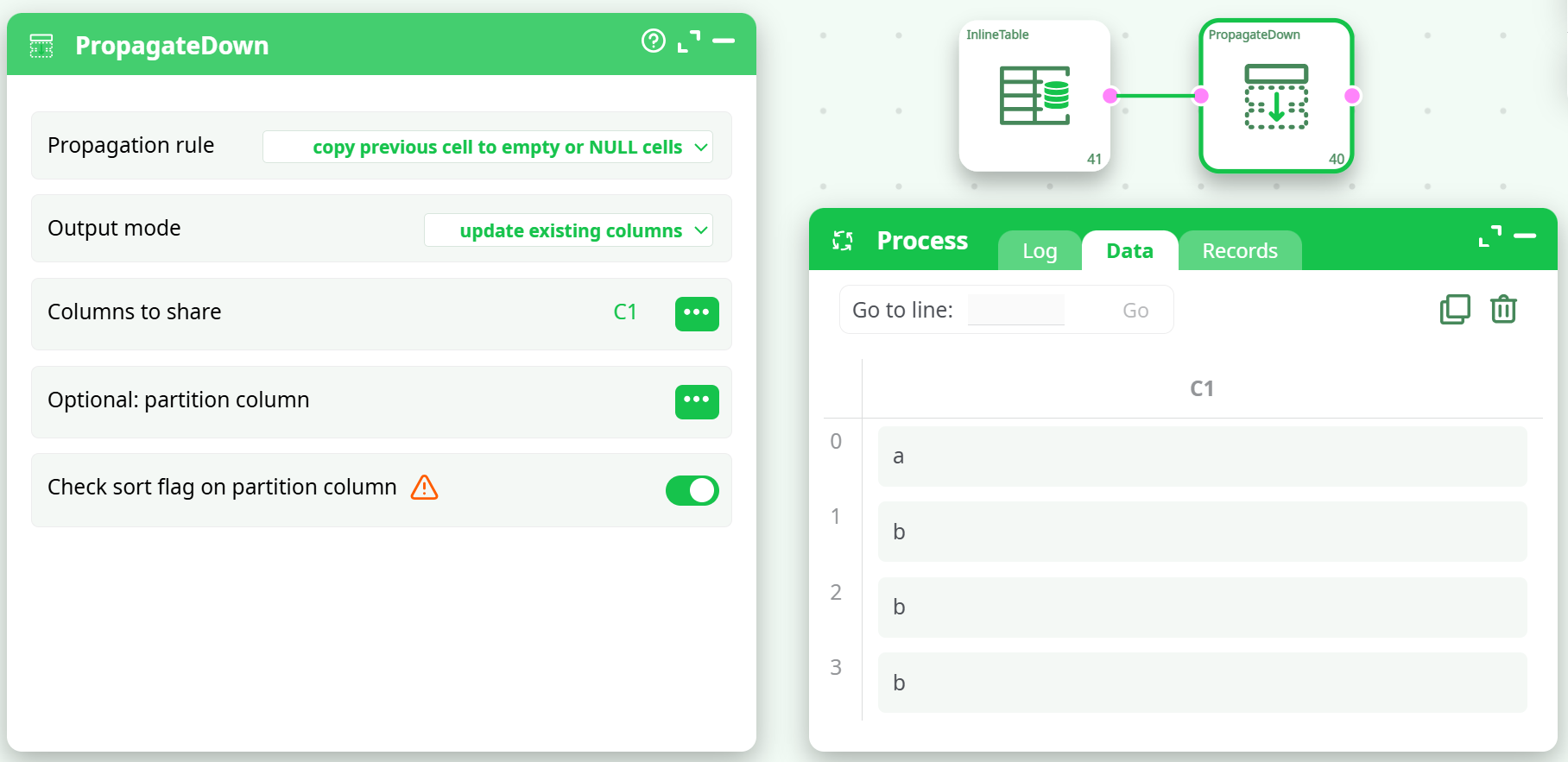
Input (C1):

With parameters:
- Propagation rule: copy previous cell to empty or NULL cells
- Output mode: update existing columns
Result:
Example Scenario:
You receive transactional data exported from a system in the following format:
| Date | Transaction |
|---|---|
| 2025-06-01 | Purchase A |
| Purchase B | |
| Purchase C | |
| 2025-06-02 | Purchase D |
After applying PropagateDown on the Date column, the result is:
| Date | Transaction |
|---|---|
| 2025-06-01 | Purchase A |
| 2025-06-01 | Purchase B |
| 2025-06-01 | Purchase C |
| 2025-06-02 | Purchase D |
This transformation ensures that all rows contain a complete context, allowing downstream processes such as grouping, filtering, or exporting to function correctly.
NOTE
- Always use the partition column if your data has grouped structures to avoid incorrect propagation across unrelated data blocks.
- Use create new columns mode for auditability if you want to preserve original column values.
- If data is unsorted, consider sorting before using PropagateDown for correct results.